Introduction
Acetaminophen is one of the most common over-the-counter medications you’ll find in any household. It’s the go-to for relieving headaches, reducing fevers, and easing minor aches and pains. But how much do you know about this seemingly simple drug? Let’s dive deep into the world of acetaminophen and uncover everything from its chemical makeup to its environmental impact.
- What is Acetaminophen?
Acetaminophen, also known as paracetamol in some parts of the world, is a pain reliever and a fever reducer. Chemically, it’s known as N-acetyl-p-aminophenol. Discovered in the late 19th century and first marketed in the mid-20th century, acetaminophen has become a staple in pain management.
How Acetaminophen Works
Understanding how acetaminophen works can give you a better appreciation of its effects. Essentially, it inhibits the production of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that promote inflammation, pain, and fever. Unlike NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), it doesn’t reduce inflammation but effectively targets pain and fever.
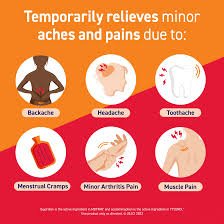
Common Uses of Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is versatile:
Everyday Pain Management: It’s perfect for headaches, muscle aches, arthritis, and backaches.
Fever Control: It’s reliable for reducing fever in adults and children.
Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain: Often recommended for managing pain after surgeries or for chronic conditions.
Dosage and Administration
Getting the dosage right is crucial:
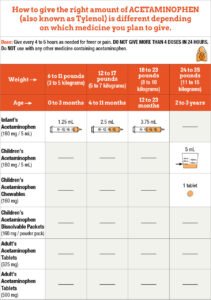
Recommended Dosages: Adults typically can take 500-1000 mg every 4-6 hours, but should not exceed 4000 mg in 24 hours. For children, dosages are based on weight.
Forms: Available in tablets, liquid, chewable tablets, and suppositories.
Guidelines for Safe Usage: Always follow the instructions on the label or those given by a healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects
While generally safe when used correctly, acetaminophen can cause side effects:
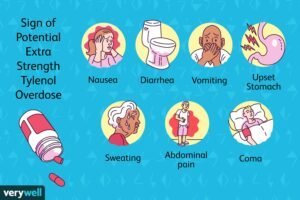
Common Side Effects: Nausea, stomach pain, loss of appetite, itching, rash, and headache.
Rare but Serious Side Effects: Liver damage, allergic reactions, severe skin reactions.
Long-Term Use Implications: Chronic use, especially at high doses, can lead to serious liver damage.
Myths and Misconceptions
Let’s bust some common myths:

Myth 1: “Acetaminophen is completely safe at any dose.” Fact: Overdosing is dangerous.
Myth 2: “It can be taken with any medication.” Fact: Many interactions exist.
Myth 3: “It’s an anti-inflammatory.” Fact: It reduces pain and fever but not inflammation.
Conclusion
Acetaminophen is a powerful tool in managing pain and fever, but it’s not without its risks. Understanding how to use it safely and effectively can make a significant difference in your health. Always follow dosage guidelines, be aware of potential side effects, and consult with healthcare professionals as needed.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE INFORMATION
FAQs
- Can I take acetaminophen with alcohol?
It’s best to avoid alcohol while taking acetaminophen, as it can increase the risk of liver damage.
- Is acetaminophen safe for children?
Yes, but the dosage should be adjusted according to the child’s weight and age. Always follow the pediatrician’s advice.
- What should I do if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next dose. Don’t double up to make up for the missed dose.
- How long does it take for acetaminophen to work?
It usually starts working within 30 to 60 minutes, providing relief from pain and reducing fever.
- Can acetaminophen be used for chronic pain?
It can be used for chronic pain, but long-term use should be monitored by a healthcare professional to avoid potential risks.