Introduction

Concern over mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, has grown in recent years. It’s critical to comprehend malaria’s symptoms, transmission mechanisms, and preventative measures as new cases emerge globally. This blog will go into these areas, simplifying and putting difficult medical information into understandable terms.
What is Mpox?

The virus that causes mpox is the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus. The disease was initially identified in 1958 in study monkeys, which is why it got its name. It is crucial to remember that the virus is not limited to monkeys; humans and rats are among the many other mammals it can infect.
How Does Mpox Spread?

The main way that mpox is transmitted is by intimate contact with an infected person or animal. The virus can enter the body via broken skin, the respiratory system, or mucous membranes (mouth, nose, or eyes). Here are a few typical ways that the mpx can spread:
1. Human-to-Human Transmission:
Direct contact with the body fluids, skin lesions, or respiratory droplets of an infected individual causes this. Extended direct eye contact, such as kissing or living next to one another, can help spread the infection.
2. Animal-to-Human Transmission:
By handling or eating infected animals, especially rats or monkeys, humans can get mpox. Bite wounds, scratches, and contact with the animal’s blood, bodily fluids, or lesions can all result in the virus spreading.
3. Indirect Contact:
Contact with contaminated objects, including as clothing, bedding, or surfaces that have come into contact with an infected human or animal, can also spread the mpox virus.
Symptoms of Mpox
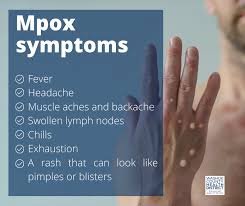
Mpox symptoms typically begin 5 to 21 days after exposure, with the illness progressing through several stages:
- Initial Symptoms (Prodromal Phase): Early symptoms resemble the flu and include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, backache, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. This phase usually lasts 1 to 5 days.
- Rash Development: After the initial symptoms, a rash appears, often starting on the face before spreading to other parts of the body, including the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash progresses through several stages:
- Macules: Flat, discolored spots on the skin.
- Papules: Raised bumps that are often itchy.
- Vesicles: Small, fluid-filled blisters.
- Pustules: Larger, pus-filled lesions.
- Scabs: The pustules eventually scab over and fall off.
- Recovery: The illness typically lasts 2 to 4 weeks. Once the scabs fall off, the person is considered no longer infectious.
Complications of Mpox

Although mpox is usually a self-limiting illness that goes away on its own, it can occasionally cause serious problems, particularly in children, pregnant women, and people with compromised immune systems. Possible complications include:
- Secondary Infections: Skin lesions can become infected with bacteria, leading to secondary infections.
- Respiratory Issues: In severe cases, the virus can affect the respiratory system, causing breathing difficulties.
- Corneal Infections: If the eyes are affected, it can lead to corneal infections and potentially cause vision problems.
How is Mpox Diagnosed?

A combination of laboratory testing and clinical assessment is used to diagnose mpox. To confirm the presence of the virus, a healthcare provider may take samples from skin lesions, respiratory secretions, or blood if they have reason to believe that the patient may have Mpox based on symptoms and potential exposure. PCR testing, or polymerase chain reaction, is the most widely used technique for identifying the monkeypox virus.
Treatment Options for Mpox

Currently, there is no specific treatment for Mpox. Most cases are mild and recover with supportive care, which focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Treatment options include:
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce fever and alleviate discomfort.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids is essential to prevent dehydration, especially if fever or rash is severe.
- Antibiotics: If a secondary bacterial infection develops, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Antiviral Drugs: In severe cases or for individuals at high risk of complications, antiviral drugs like tecovirimat (TPOXX) may be considered under special circumstances.
Preventing Mpox: What You Can Do

Prevention is key when it comes to Mpox. Here are some steps you can take to protect yourself and others:
- Avoid Close Contact: Limit contact with people who are infected or show symptoms of Mpox, especially if they have a rash.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): If caring for someone with Mpox, use gloves, masks, and other protective gear to minimize exposure.
- Avoid Handling Animals: Refrain from handling animals that could be carriers of the virus, particularly in regions where Mpox is endemic.
- Vaccination: In certain situations, healthcare providers may recommend the smallpox vaccine, which provides some protection against Mpox due to the similarities between the two viruses. CLICK HERE FOR MORE INFORMATION
Conclusion:
Due to recent outbreaks, mumps is a rare but potentially dangerous viral virus that has received attention. Reducing the risk of infection requires knowledge of the symptoms, how it spreads, and self-defense techniques. Although the majority of mpox cases are mild and self-limiting, early detection and treatment can avert problems and halt the virus’s transmission.
https://youtu.be/5m0wZuuo7DY?si=A7O-AUj3AARl3Z1V
FAQs
- Can Mpox be fatal?
In most cases, Mpox is not fatal. However, it can lead to severe complications in some individuals, especially those with weakened immune systems. - How is Mpox different from smallpox?
Mpox is caused by a virus related to, but less severe than, the smallpox virus. Smallpox has been eradicated, while Mpox continues to occur, mainly in Africa. - Can Mpox be transmitted through the air?
While Mpox can spread through respiratory droplets, it typically requires prolonged face-to-face contact, unlike more easily airborne viruses. - Is there a vaccine for Mpox?
The smallpox vaccine can offer some protection against Mpox, but it is not widely used for this purpose due to the low risk of infection in most regions. - What should I do if I think I have Mpox?
If you suspect you have Mpox, seek medical advice immediately. Isolate yourself to prevent spreading the virus to others.